Protein Drawing Biology
Protein Drawing Biology - The ribbon depicts the general course and organisation of the protein backbone in 3d and serves as a visual framework for hanging details of the entire. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, exactly the same from one molecule to the next. Web in fact, structure prediction can be considered a form of conditional protein design if the conditioning variable is the sequence of the protein itself. They may serve in transport, storage, or membranes; Create science figures in minutes with biorender scientific illustration software! Have you ever seen a. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The n terminal amino acid of the a chain is glycine, whereas the c terminal amino acid is asparagine (figure 1). The first of these is the primary structure, which is the number and sequence of amino acids in a protein’s polypeptide chain or chains, beginning with the free amino group and maintained by the peptide bonds connecting each amino acid to the next. It is much easier to see what is happening if you do that. Browse 1000s of icons & templates from many fields of life sciences. Web proteins are essential for the main physiological processes of life and perform functions in every system of the human body. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Ribbon diagrams, also known as richardson diagrams, are 3d. Your folded paper should look like this. Web proteins that extend all the way across the membrane are called transmembrane proteins. They may serve in transport, storage, or membranes; The portions of an integral membrane protein found inside the membrane are hydrophobic, while those that are exposed to the cytoplasm or extracellular fluid tend to be hydrophilic. Open the top. However, for drawing the structures of proteins, we usually twist it so that the r group sticks out at the side. Browse 1000s of icons & templates from many fields of life sciences. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. There are four levels of protein structure; The primary structure, the secondary structure, the tertiary structure, and the quaternary structure. Web the structure of proteins is generally described as having four organizational levels. The portions of an integral membrane protein found inside the membrane are hydrophobic, while those that are exposed to the cytoplasm or extracellular fluid tend to be hydrophilic. Explain how mrna is processed before it leaves the nucleus. Web proteins are one of the most abundant organic. The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. Open the top layer and flatten it. The first of these is the primary structure, which is the number and sequence of amino acids in a protein’s polypeptide chain or chains, beginning with the free amino group and maintained by the peptide bonds connecting each amino. Web start making professional scientific figures today. The primary structure, the secondary structure, the tertiary structure, and the quaternary structure. The function of a protein is highly dependent on its 3d structure. Identify the steps of transcription, and summarize what happens during each step. Web the structure of proteins is generally described as having four organizational levels. The portions of an integral membrane protein found inside the membrane are hydrophobic, while those that are exposed to the cytoplasm or extracellular fluid tend to be hydrophilic. Proteins are therefore also known as polypeptides. Your folded paper should look like this. Proteins may be structural, regulatory, contractile, or protective. Web proteins come in many different shapes and sizes. Web proteins are essential for the main physiological processes of life and perform functions in every system of the human body. Have you ever seen a. The custom texture mapping and lighting calculations for rendering these images are implemented using vertex and fragment. Create science figures in minutes with biorender scientific illustration software! The portions of an integral membrane protein. Web proteins are essential for the main physiological processes of life and perform functions in every system of the human body. To understand how a protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand the four levels of protein structure: Web as we mentioned in the last article on proteins and amino acids, the shape of a protein. Your folded paper should look like this. Function is a lot trickier because it’s. Proteins are composed of amino acid subunits that form polypeptide chains. Web protein folding and structure. Web taken together, we propose that dog 1.0 could be a great help for molecular and cellular experimentalists, allowing the presentation of protein domain structures in a more precise, convenient. Function is a lot trickier because it’s. So when you see a “picture” of a protein, you are really looking at a drawing or computer model of the protein’s structure. Have you ever seen a. The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. The ribbon depicts the general course and organisation of the protein backbone in 3d and serves as a visual framework for hanging details of the entire. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. It is much easier to see what is happening if you do that. Web the primary structure of proteins. Web as we mentioned in the last article on proteins and amino acids, the shape of a protein is very important to its function. Web a set of tools for generating high quality raster images of proteins or other molecules. Web proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Your folded paper should look like this. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, exactly the same from one molecule to the next. Some are globular (roughly spherical) in shape, whereas others form long, thin fibers. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, a and b, and they are linked together by disulfide bonds. Unfold the top layer halfway./protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
Four Types of Protein Structure
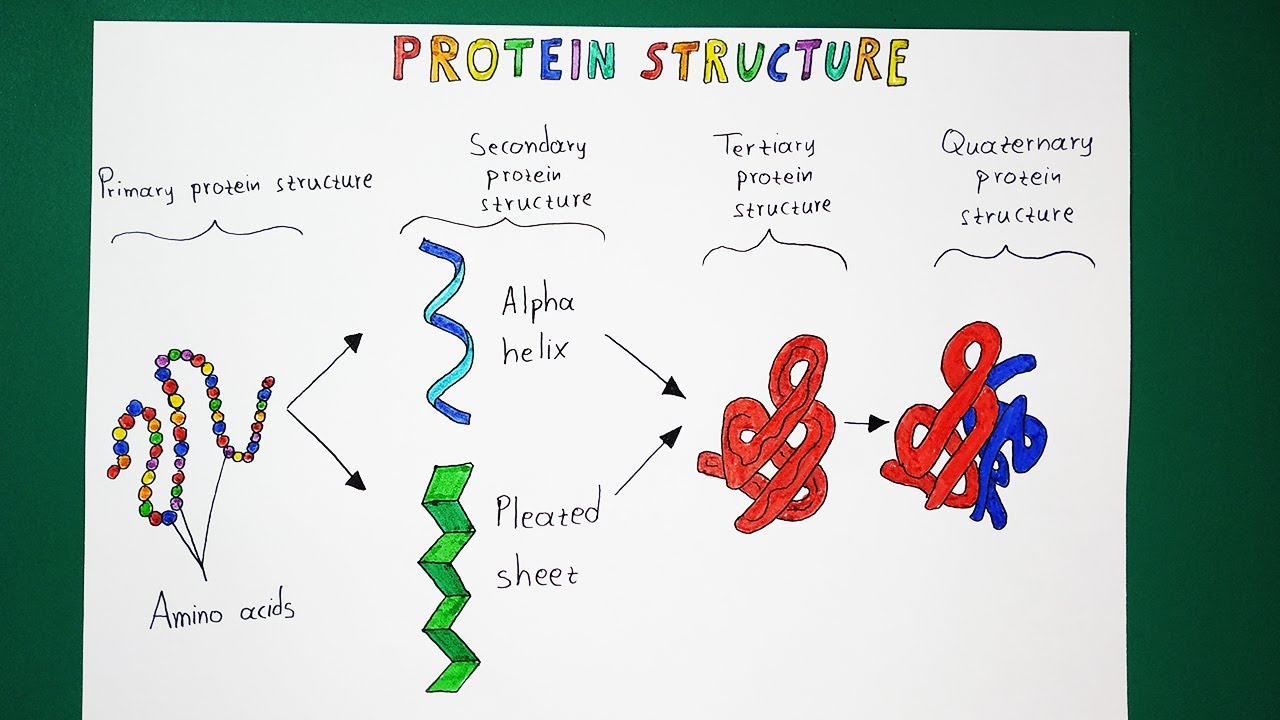
Protein Structure Levels From Amino Acid To Complex Molecule Outline

Protein Illustrations and Visualization Ask A Biologist
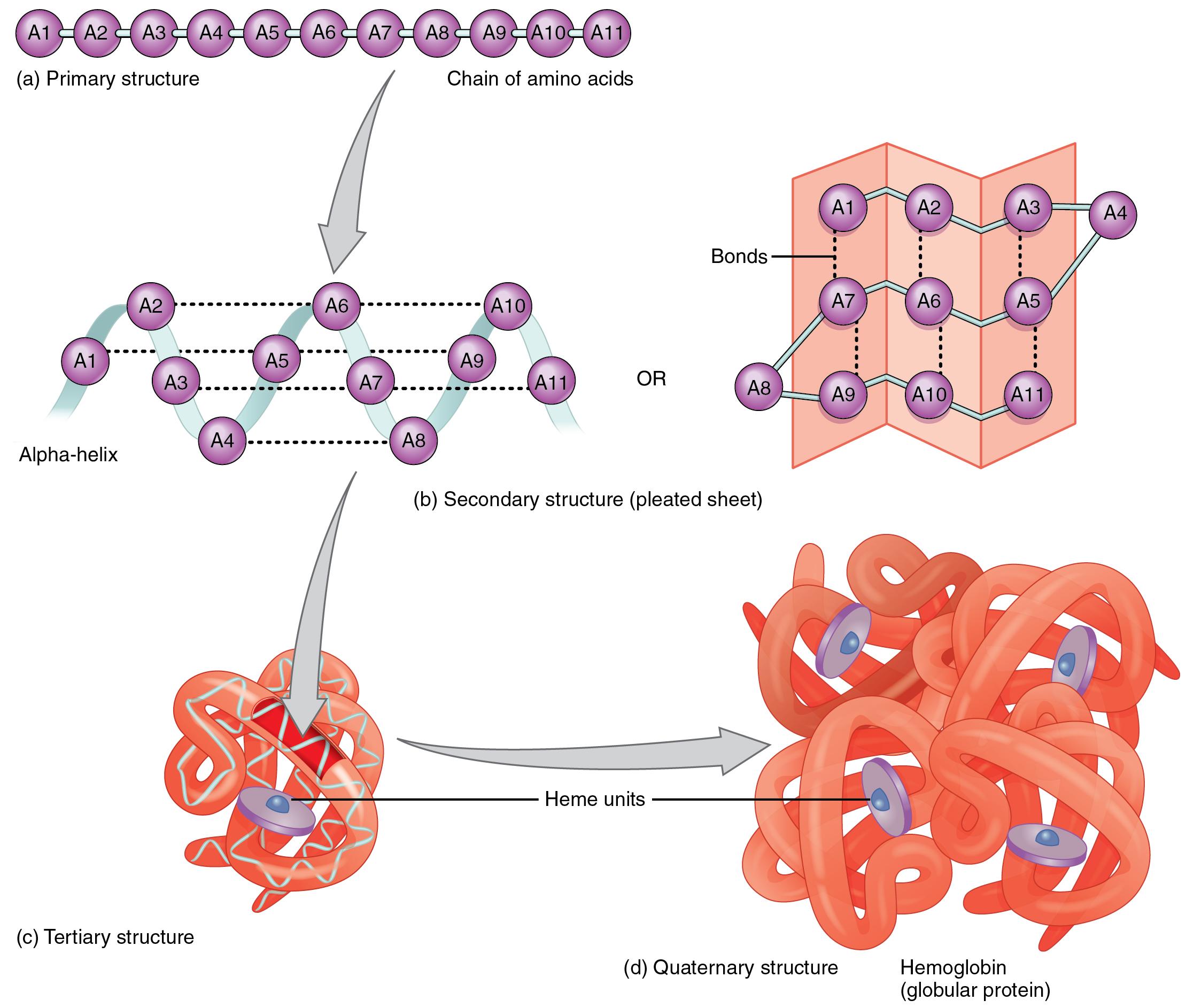
2.23 Protein Structure Nutrition Flexbook
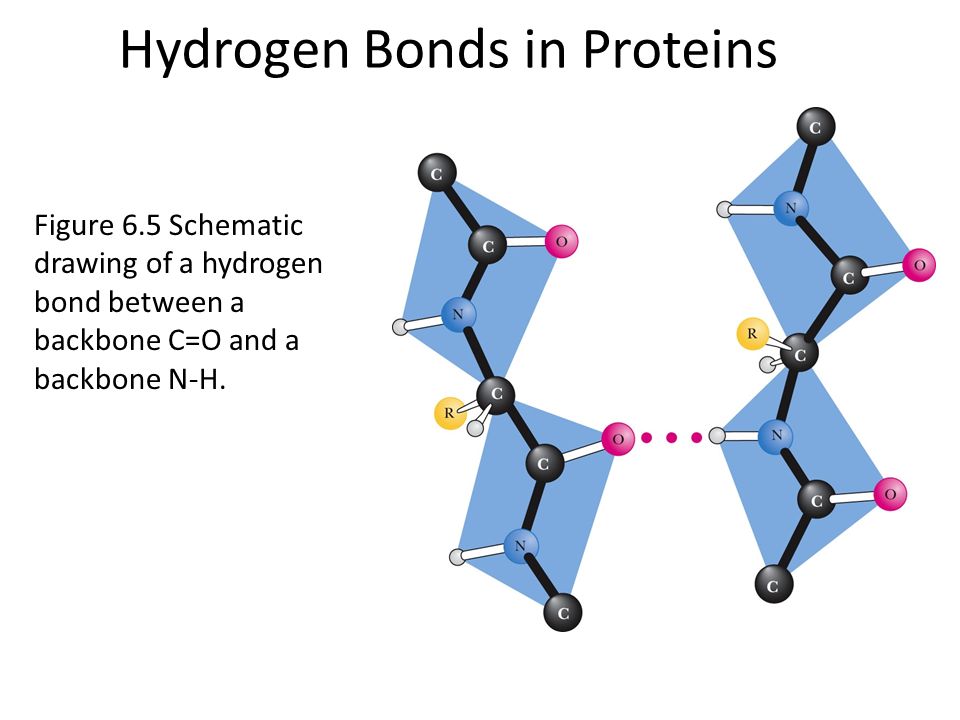
Proteins Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Glossary Protein Structure Class 1

The Basics of Protein Structure and Function Interactive Biology

Cell Biology Glossary Membrane Proteins Draw It to Know It

Understanding Proteins and How They Are Made DOES GOD EXIST? TODAY
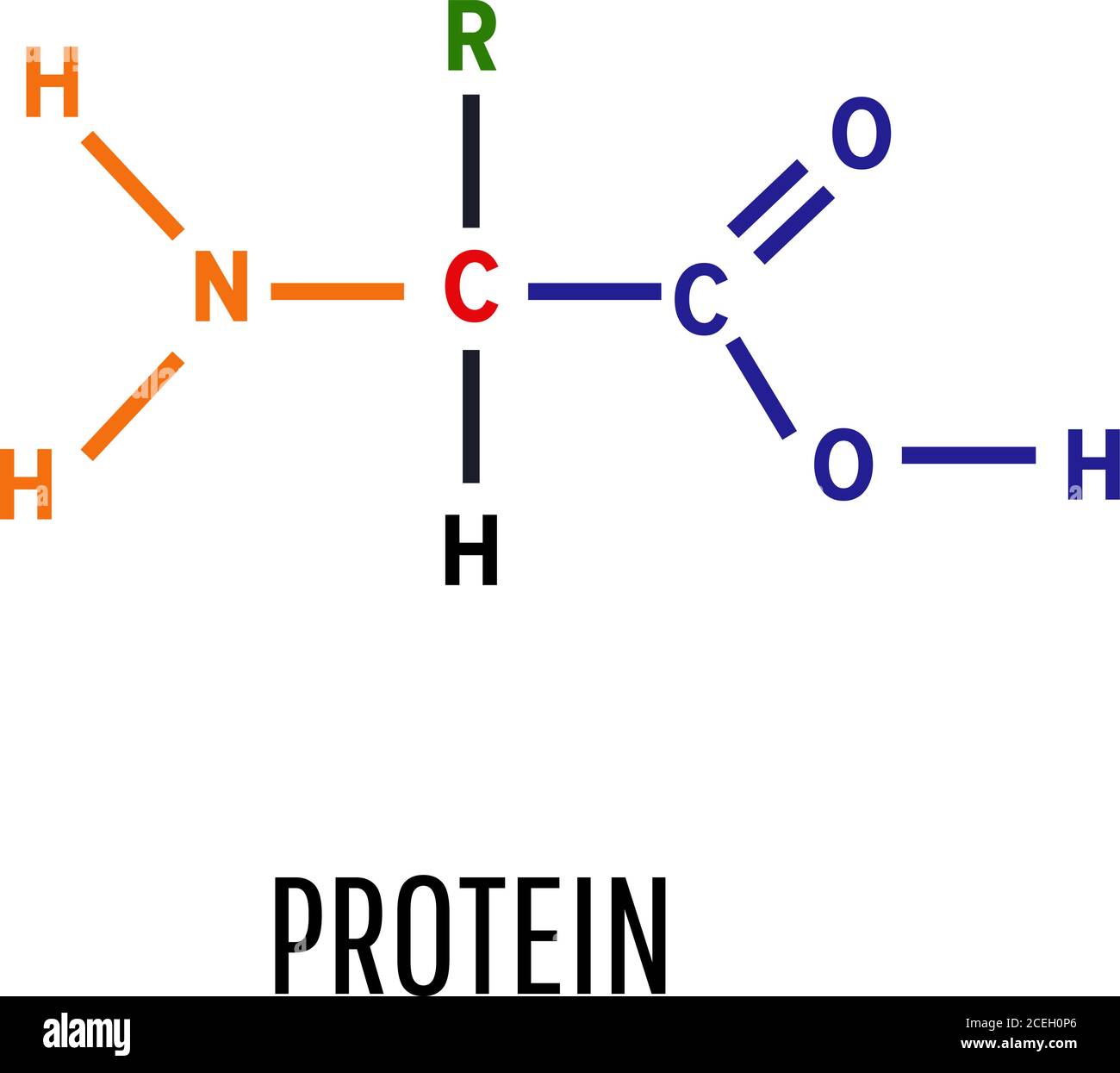
Protein. Structural chemical formula and molecular model. General
Identify The Steps Of Transcription, And Summarize What Happens During Each Step.
Ribbon Diagrams, Also Known As Richardson Diagrams, Are 3D Schematic Representations Of Protein Structure And Are One Of The Most Common Methods Of Protein Depiction Used Today.
However, For Drawing The Structures Of Proteins, We Usually Twist It So That The R Group Sticks Out At The Side.
Circular Pieces Of Dna Commonly Used In Molecular Biology.
Related Post: